Dyspnea is also known as difficulty breathing or shortness of breath. It refers to an uncomfortable awareness of breathing. Dyspnea is more of a symptom than a disease and, therefore, usually points toward an underlying condition of the body. Shortness of breath can be manifested acutely or chronically, mild or severe, due to physical exertion, environmental factors, or other pathologic causes. Thus, early identification of its signs, with ensuing correct intervention, has paramount importance.
This article describes the causes of dyspnea, the symptoms of dyspnea, and treatment methods that range from acute dyspnea to chronic dyspnea.
Table of Contents
What is Dyspnea?
Dyspnea is the perception of an abnormal difficulty of breathing. Patients with such issues usually describe chest tightness, shortness of breath, or a smothering feeling. It should be realized that this illness is a subjective feeling, and in one patient this may cause extreme discomfort, whereas another individual may experience only slight or no distress under similar conditions.
Causes of Dyspnea
Dyspnea can emanate from several causes. The etiologies can then be broadly categorized into five main groups: respiratory, cardiac, neuromuscular, psychological, and environmental. Many of the causes are acute and require immediate medical attention; others will lead to chronic dyspnea and, thus, management.
1- Respiratory Causes
Most causes of this issue arise from the lungs. These include:
(a)-COPD-Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
This is a collection of lung diseases, such as chronic bronchitis and emphysema, which cause breathlessness. In COPD, the airways are swollen, and the lung tissue is damaged, making a person short of breath.
(b)-Asthma
This is a chronic disease of the lungs wherein airways narrow, swell, and make extra mucus, thus making a person feel difficulty breathing.

(c)-Pneumonia
Infection of the air sacs in one or both lungs, which fills them up with pus or fluid. Symptoms are shortness of breath, chest pain, and cough. A pulmonary embolism is a sudden blockage in one of the arteries that carries blood to the lungs. Usually, blockage is due to a blood clot. Symptoms may include acute and severe dyspnea.
(d)-Interstitial Lung Disease
A bunch of disorders that cause scarring of lung tissue. The symptoms, resulting from this, include long-term breathing problems.
(e)-Pneumothorax
Collapse of a lung due to leakage of air into the intrapleural space caused by penetrating injury to the chest leading to sudden breathlessness and pain in the chest.
2- Cardiac Causes
Other common causes are disorders in the cardiovascular system; this is because both the heart and lungs are very closely related in the mission to supply oxygen to the body. Principal cardiac conditions that can cause it include:
(a)- Heart Failure
Then again, in the event of the heart’s malfunctioning as a pump to circulate enough blood to meet the body’s demand for it, the fluid backs up into the lungs, causing difficulty or labored breathing.
(b)- CAD (Coronary Artery Disease)
It may be manifested by such issue especially on exertion due to narrowed or blocked coronary arteries; this leads to reduced blood flow to the heart muscle.
(c)- Pericarditis
is an inflammation of the pericardium, the fluid-filled sac surrounding your heart. It can lead to chest pain and difficulty breathing.
3- Neurological Causes
This is dyspnea resulting from ailments of the muscles and nerves that control breathing, including the following:
(a)- ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis)
a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects the muscles responsible for breathing.
(b)- Myasthenia Gravis
A chronic autoimmune disorder marked by muscle weakness, including the muscles necessary to breathe.
4- The psychological causes
include anxiety and panic disorders, which may occasion such illness or deteriorate its symptomatology. An anxious or panic attack victim can easily start hyperventilating, thus feeling dyspneic. A vicious cycle can thus be instituted, with this issue fueling the anxiety and vice versa, further increasing the sensation of breathlessness.
5- Environmental Causes
These include extreme elevations, air pollution, and even allergens inhaled. Other activities that might cause temporary issues of shortness of breathing include strenuous exercise-particularly among those individuals not usually undergoing such physical exertion.
Symptoms of Dyspnea

Symptoms will, of course, depend on the cause, the severity of the condition, and whether the shortness of breathing is considered to be an acute or chronic problem. General symptoms, however, include:
Shortness of breath
a sensation of not taking a full breath, or as though you are not getting enough air.
Tightness in the chest
A feeling of pressure or squeezing in the chest that makes breathing uncomfortable.
Tachypnea(Rapid Breathing)
More rapid breathing than normal, often as a compensatory mechanism when the body feels deprived of oxygen.
Wheezing
A whistling or squeaky sound while breathing, is typically caused by narrowed airways.
Fatigue
Shortness of breath can make even the simplest tasks exhausting. Air hunger: A strong urge to breathe, often accompanied by anxiety or panic.
Coughing
A dry or productive cough is especially present when shortness of breath is related to respiratory infections such as pneumonia. Shortness of breathing can be either sudden in onset or gradual in development.
Acute Dyspnea
Acute dyspnea is a sudden onset of shortness of breath and might need immediate medical attention. It may result from the following:
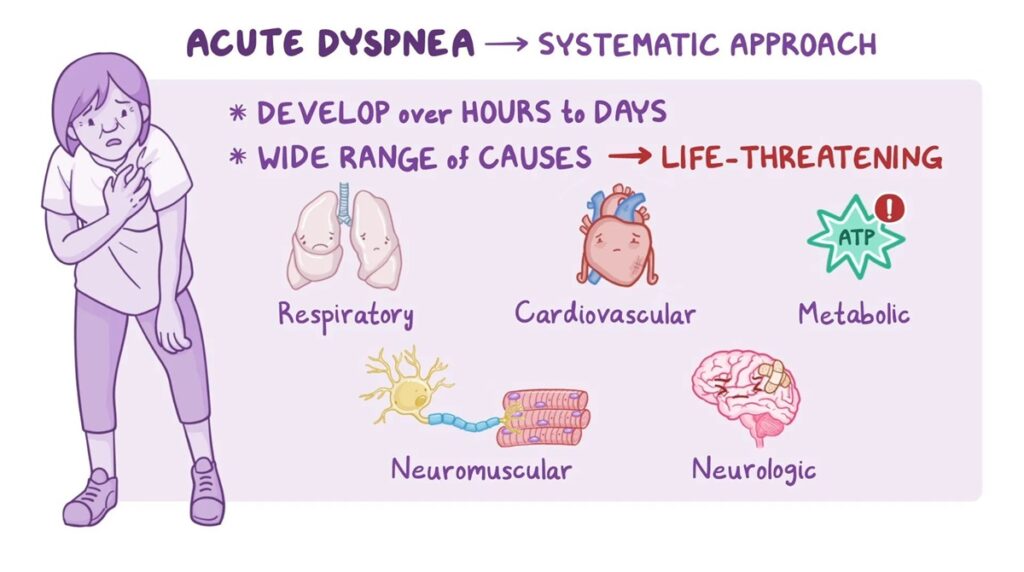
Pulmonary Embolism: The sudden blockage of an artery within the lungs, usually due to clots elsewhere in the body, is life-threatening except when treated.
Myocardial Infarction: A reduction of the flow of blood to the heart muscle causes severe chest pain together with shortness of breath and a feeling of doom.
Pneumonia: This is a sudden lung infection, developing over an extremely short period, which may be associated with the potential for extreme shortness of breath.
Asthma Attack: A sudden increase in asthma symptoms leading to severe narrowing of the airways and difficulty breathing.
Acute dyspnea is often treated urgently to avoid serious complications or death. Such life-threatening dyspnea treatments may involve oxygen therapy, medications to reduce inflammation in the airways, or surgery, which may be necessary depending on the cause, for instance, pneumothorax.
Chronic Dyspnea
Chronic dyspnea is a long-term condition wherein breathlessness can continue for weeks or even months. Long-term chronic conditions which have shortness of breath as part of their symptomatology include:
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): A progressive condition wherein, over time, the difficulty in breathing deteriorates and long-term dyspnea is realized.
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF): A condition wherein the heart cannot pump properly. Fluid builds up inside the lungs, creating chronic shortness of breath.
Obesity: The added weight puts strain on the lungs and diaphragm; hence, dyspnea can be caused by minimal exertion.
Anemia: An inadequacy of red blood cells or hemoglobin allows less oxygen to be circulated to the tissues, thus giving a sensation of not having enough breath.
Management of chronic dyspnea should be multidisciplinary, addressing the underlying cause of the problem, while focusing on the improvement in the quality of life.
Dyspnea Treatment

The modality of treatment for shortness of breath would depend upon the etiology, severity, and chronicity or acuteness of the shortness of breath. The goals of treatment involve symptom relief, causality management, and the enhancement of the patient’s activities of daily living.
1-Oxygen Therapy: Severe dyspnea, especially those from cardiac or respiratory-related disorders, would respond well to supplemental oxygen administration, which would increase oxygenation of the blood and eventually reduce the sensation of shortness of breath.
2-Medication:
Bronchodilators and corticosteroids are drugs used in the management of asthma, COPD, and other varieties of lung conditions. They dilate the airway and reduce inflammation to create ease of breathing.
Diuretics: These are drugs that may be used in heart failure to alleviate fluid overload in the lungs associated with dyspnea.
Anticoagulants: This is a form of medication through which medication is administered in the form of blood-thinning drugs for conditions such as pulmonary embolism, which helps dissolve clots to restore normalcy in the lungs.
3-Respiratory Therapy: Symptoms of dyspnea may be relieved by breathing techniques, such as pursed-lip and diaphragmatic breathing, which tend to alleviate chronic dyspnea since there will be an improvement in the efficiency of the lungs and less anxiety. These exercises are also included in pulmonary rehabilitation programs since these are ways to strengthen the lungs and build stamina
4- Life Style Modifications
Smoking Cessation: Smoking is the leading cause of respiratory diseases due to dyspnea; these include COPD and lung cancer. Cessation can reduce the progression of lung disease by significantly improving breathing.
Control of body weight: The elimination of excess body weight removes pressure from the diaphragm and lungs, reducing the chronic shortness of breath.
Exercise: The control and slow exercise allow for improving the cardiovascular and respiratory systems to allow the chronic dyspnea patient to regain muscle strength and reduce their symptoms.

5-Surgical Interventions: These are utilized in the worst cases. For instance, a pneumothorax may necessitate the insertion of a chest tube or surgical intervention to aspirate air from the pleural space. Lung transplantation may be considered for patients with severe lung disease.
6-Psychological Interventions: Therapy, including CBT, may be of benefit in aiding patients with anxiety or panic disorders to develop coping strategies to manage dyspnea that is precipitated by anxiety.
Conclusion
Dyspnea is the medical term for difficulty breathing, which becomes a symptom that causes unease and may emanate from a wide range of causes, including respiratory, cardiac, and psychological. Therefore, knowing the causes of dyspnea, recognizing symptoms of dyspnea, and getting appropriate dyspnea treatment becomes vital to keep both acute dyspnea and chronic dyspnea in check.
Whereas some conditions have been considered to necessitate immediate treatment, other conditions call for long-term lifestyle changes or therapies that could enhance the quality of one’s life. Generally, timely diagnosis and treatment are a cornerstone in approaching the root causes for improvements in health outcomes.
Disclaimer
In this article, information related to a particular topic has been collected from various sources, the purpose of which, is only to increase the knowledge of the readers and it does not confirm the existence of any disease, particular statement, explanation, appropriateness, congruity, and information or any kind of treatment. Health Alpha does not take any responsibility for any such information.
Views: 6