Each year, millions of people die from cancer. Whether male or female, young or aged, the case of cancer and its risk factors appear in all. The most commonly reported cases in men are of lung and prostate cancers, while women most commonly report breast, ovarian, and cervical cancers.
In the data provided, cancer-related deaths amounted to 76.4 for every 100,000 people in 2022. Ovarian and cervical cancers remained to be the most frequent causes of death by cancer for females and breast cancer remained to be first in line with others in rank.
Table of Contents
However, some relief news is coming out to minimize this cancer risk in women. Researchers from Oxford University state that the first-ever vaccine for this cancer is going to be developed in the UK. Scientists are hopeful that the vaccine is going to help get rid of risks associated with this deadly disease.
If the vaccine proves effective during trials, then millions of deaths due to this ovarian cancer are likely to be prevented annually.
Vaccine for ovarian cancer
The team of scientists has named this vaccine ‘Ovarianvax’. According to experts, this vaccine will be given to women as a preventive measure against cancer. It has been modeled in the same way as the HPV vaccine for cervical cancer.
According to reports, the vaccine is being manufactured in such a way that the body’s immune system catches this cancer at the very beginning and prevents or destroys the cancer cells from growing.
The vaccine will recognize cancer cells
Giving information about the Ovarianvax vaccine, According to Dr. Ahmed, director of the cell laboratory of Ovarian Cancer at Oxford University, this vaccination would prove itself as a cellular target. Researchers are trying to discover the proteins the vaccination most rapidly identifies with chances of occurring within cancer cells in the primary stages of their formation. Work will be done on the identification of the cancer-causing vaccine at a more advanced stage.
What do scientists say?
Dr Ahmed says, if the vaccine is successful then its results can be seen within the next five years. These vaccines can help reduce this major health risk globally. We aim to eliminate this cancer, it is hoped that this vaccine can give very good results in this direction. Although we still have a long way to go.
The vaccine aims to boost the immune system to recognize more than 100 proteins on the surface of this cancer.
The risk of ovarian cancer is increasing in India too
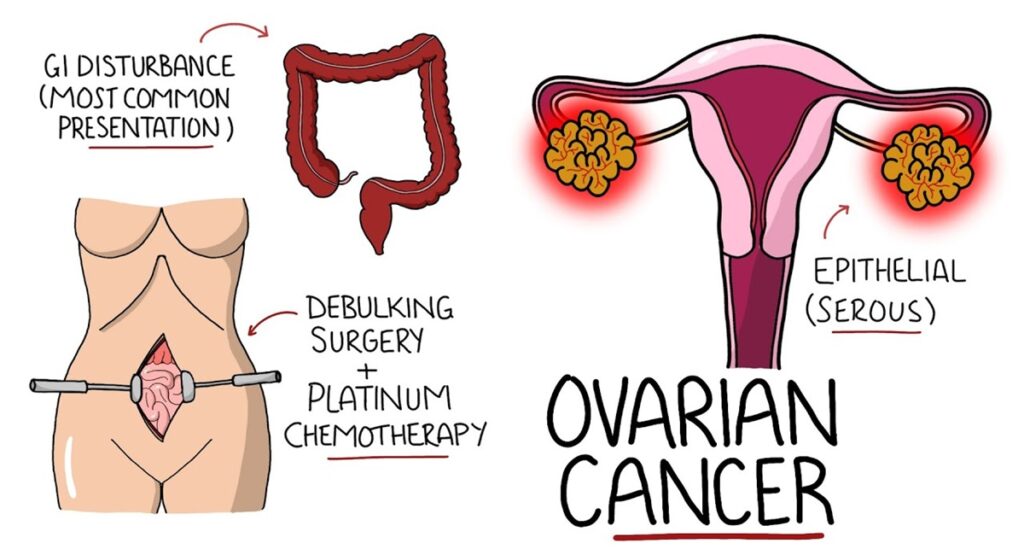
Ovarian cancer is a cause of serious concern in many cases. For Indian women, it is the third most frequent type of cancer. Since there is no specific screening test for this cancer and the symptoms can be similar to other stomach diseases, it is not diagnosed in time.
Dr David Crosby, head of research at Cancer Research UK, said it could take years for any potential vaccine to be ready for widespread use. The team of scientists is optimistic about this vaccine, hoping that we can achieve success in reducing this cancer in the coming years.
Let’s Have a Light on Ovarian Cancer
Among the other cancers that affect women, ovarian cancer is one of the most aggressive and most difficult. Owing to the nonspecific symptoms, treatments may be hindered as diagnosis usually comes late in the course of the illness when it has already progressed a lot. This paper will attempt to explain the various aspects of ovarian cancer, ranging from symptoms up to treatment options, survival rates, and prevention measures, as well as discuss of some the latest breakthroughs in medicine.
What is Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer sets in when abnormal cells growing out of control in the ovaries develop a tumor. If not identified and treated early, the malignant cells may spread into other parts of the body. The female reproductive system comprises the ovaries. They are responsible for producing eggs and releasing hormones called estrogen and progesterone.
There are mainly three types of ovarian cancers.
Epithelial ovarian cancer: This is the most common type, accounting for nearly 90%. This form arises in the layer of cells covering the outer surface of the ovaries.
Germ cell ovarian cancer: This is the rarest form, which originates in cells producing eggs; it affects mainly young women.
Stromal cell ovarian cancer– occurs in the supportive tissue cells that produce hormones and combine the two ovaries.
Ovarian Cancer Symptoms: The Silent Signs
The most sensitive area in the diagnosis of ovarian cancer is its feeble, sometimes very vague appearance. Early symptoms of ovarian cancer can easily be masked to appear like the more common and less serious conditions, such as gastrointestinal problems or bladder disorders. However, if these symptoms have been persisting or worsening, they should be medically evaluated. Some of the Ovarian Cancer Symptoms include:
Abdominal bloating or swelling: Persistent bloating that does not dissipate can be a sign of ovarian cancer. This is because the tumor grows and puts pressure on the abdomen.
Pelvic pain or discomfort: A woman may suffer from chronic pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen or pelvic region.
Difficulty in eating or early satiety: A reduced appetite or feeling satisfied after having taken only a little is the most common symptom that is linked to ovarian cancer
Urination: The cancer may cause pressure on the bladder so that the patient starts urinating more frequently, or even urgently.
Unintended loss of weight: Sudden unintended weight loss may lead to suspecting ovarian cancer.
Fatigue: There is a possibility that she may feel quite drained, and there is no specific reason behind it. This is one of the earliest symptoms of ovarian cancer.
Changes in bowel habits: She might be found to be constipated or having diarrhea for a long time; this also becomes an indicator.
It must be noted that the above symptoms do not point to ovarian cancer, but their persistence over time is what is a concern. Women who regularly experience these symptoms should see a doctor because they linger much longer than any other cases, especially over several weeks.
Risk Factors of Ovarian Cancer
While the cause of ovarian cancer is unknown, recognized risk factors do enhance susceptibility for the disease to occur.
Age. Most patients diagnosed with ovarian cancer are 50 or older, and an especially higher incidence occurs after the age of menopause.
Family history of cancers: A family history of any of ovarian, breast, and colorectal cancer increases the risk. Certain genetic mutations notably BRCA1 and BRCA2 carry the highest risk.
Personal history of cancer: Cancer at another site such as breast, colorectal, or endometrial is a known increased risk for ovarian.
Fertility history: Women who have never conceived, or whose first conception is after the age of 35 years, have an increased risk slightly.
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT): Extended estrogen replacement therapy initiated after menopause increases the risk of ovarian cancer
Obesity: The findings revealed that obesity does indeed play a role in elevating the risk of ovarian cancer in women.
Diagnosis of Ovarian Cancer
At the initial stages, ovarian cancer symptoms are very vague and, therefore, difficult to diagnose. Improving prognosis and survival rate, however, is made possible only by early diagnosis. Several diagnostic instruments and methods are used to identify ovarian cancer:
Pelvic examination: During a regular pelvic examination, the doctor can make certain diagnostic tests of the ovaries by examining any abnormalities present in the ovaries.
Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS): This is a type of radiology imaging test that employs sound waves to produce images of the ovaries and all the other reproductive organs. It is mainly used in tumor detection; however, it cannot determine whether the tumor is malignant or not.
CA-125 blood test: CA-125 is a protein present in high levels in most women affected by cancer of the ovary. The test, however, does not always come out positive. Another condition that may result in a false-positive result is endometriosis.
CT Scan / MRI: Detailed imaging is feasible through procedures such as abdominal CT scans and MRIs. The extent of the malignancy and dissemination can be established.
A Biopsy: would be the only way to diagnose the patient. Sample specimen is obtained and checked if there are malignant cells. A portion of it will have to be excised just to determine the same.
Staging of Ovarian Cancer
Once ovarian cancer is established, it becomes significant to classify how far the spread of the disease has taken place. This simply refers to the determination of the stage of cancer. The stages of ovarian cancer are as listed below:
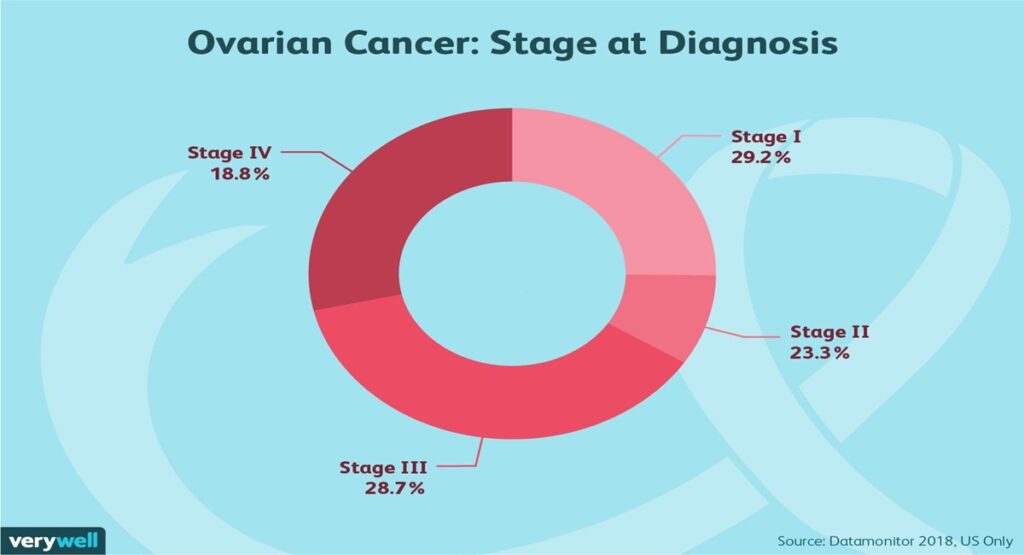
1. Stage I: the cancer is usually found within one or both ovaries.
2. Stage II: in this stage, it usually spreads to the other organs in the pelvis. The major organs that are easily affected include the uterus and/or fallopian tubes.
3. Stage III: the cancerous cells have invaded the abdominal lining or even reached the lymph nodes.
Stage IV: The cancer has already spread to some other part of the body far away from the original site in such a way that it could be in the liver or lungs.
The staging of the cancer determines part of the treatment plan along with an estimate of the prognosis.
Ovarian cancer treatment options
Treatment for ovarian cancer is determined by the stage it has been diagnosed to be at, as well as the woman’s general health and individual preference. General ovarian cancer treatment options include:
Surgery
Surgery is usually the initial treatment in case a patient is diagnosed with ovarian cancer, especially in its early stage. Surgery will often aim at removing nearly all of the cancerous tissue. These include;
Hysterectomy; this is the removal of the entire uterus
Bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy: Both ovaries and the fallopian tubes are removed.
Omentectomy: It is the surgical removal of omentum, which is fats present in the abdominal cavity. Cancer cells often also spread to this place.
Lymph node dissection: In this procedure, the adjacent lymph nodes are removed and analyzed to assess whether the malignancy can spread.
Patients with Stage I ovarian cancer can be treated through a surgery that is sort of fertility-preserving. Only one ovary and fallopian tube is removed and she is not restricted from pregnancy.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the most frequent treatment for ovarian cancer, especially when extrapelvic disease spread is present. Chemotherapy either eradicates cancer cells or ensures a considerable reduction in their rate of multiplication. Chemotherapy can be delivered through any of the following routes.
Intravenously: Chemotherapy is given into a vein in the arm.
Intraperitoneally (i.p): Infusion directly into the abdominal cavity.
Oral drug formulation: Tablet form.
Chemotherapy is sometimes used in combination with surgery-including use before the surgery, to reduce the size of the tumor before surgery, and after surgery, to eliminate any cancer cells that may have inadvertently been left behind.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted treatments target cancer cells specifically while causing the least amount of harm to healthy cells. The medicines work by suppressing molecules that help in the growth and spread of the cancer. Among the specific drugs used to treat ovarian cancer are:
PARP inhibitors: These drugs are available to only those women who are unfortunate to have the BRCA mutation. It will deprive cancer cells of their ability to repair the DNA.
Anti-angiogenic drugs: These medications, that prevent the newly formed vessels, prevent the growth and spread of the tumor.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation treatment is a type of cancer treatment, and in this treatment, a dose of radiation is administered to the patient that kills all the current cells of the cancer.
This approach is infrequently used as an initial treatment in ovarian cancer; however, it is sometimes prescribed for patients with localized ovarian tumors but which cannot be removed by surgery.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy stands out as a promising approach whereby the battle with cancer is carried out inside the body, utilizing the human immune system. Still in its infancy, this mode of therapy holds promise for ovarian cancer, as it has managed, to some extent, to overcome other cancers.
Ovarian Cancer Survival Rate
The ovarian cancer survival rate depends on the clinical stages diagnosed. This also tends to be affected by the health condition of the involved woman and some intrinsic characteristics of the tumor itself. To put it simply, the more advanced the cases detected, the lesser the chances of survival.
A five-year survival rate is a measure of the survival of cancer patients. It means the survival of at least five years after the time the cancer has been found. According to the American Cancer Society, “Five-year Survival Rate for Ovarian Cancer by Stage”
Stage I: Around 92%.
Stage II: About 70%.
Stage III: About 39%.
Stage IV: About 17%.
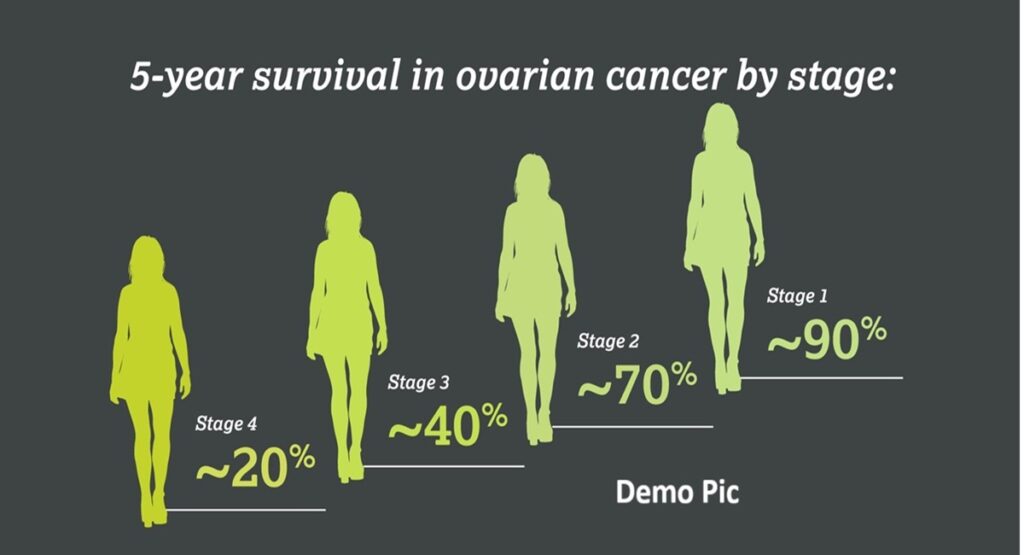
Survival rates point out the importance of early detection. Unfortunately, because of the insidious nature of the disease, ovarian cancer presents with symptoms that are mistaken for other conditions, and also may not be perceived as they appear; therefore, most women are diagnosed when their cancers have developed into more advanced stages, bringing the survival rate down significantly.
Developments in Ovarian Cancer Research
There are many such studies conducted currently, that address new treatment options and early detection of ovarian cancer. Areas of research include the following:
Biomarkers for Early Detection: Biomarkers are substances in the body whose presence could be used to predict or diagnose diseases. Therefore, the identification of specific biomarkers for the early detection of ovarian cancer will increase the chances of survival.
Improved targeted therapies: The new targeted therapies are developed that can effectively destroy cancer cells with minimal side effects of treatment and therefore improve the survival chance of a patient.
Genetic testing: Those women with a family history of ovarian cancer or bearing the BRCA mutation can undergo genetic testing to assess the level of risk. This thus permits personalized preventative and monitoring procedures.
Immunotherapy trials: This is immunotherapy which enhances the immune system’s ability to recognize and kill more cancer cells. These are currently being tested in clinical trials to determine if they could be used to treat ovarian cancer more effectively. It is therefore still in its experimental stage, but promising a lot towards becoming one of the alternative treatments for the future.
Preventive measures and the reduction of risk
While no one knows the cause of ovarian cancer or how to prevent it, various measures do appear to lower the risk for some patients:
Oral contraceptives– Birth control pills Long-term use will reduce a woman’s risk of ovarian cancer Women can decrease their risk by as much as 50 percent if they use oral contraceptives for five or more years.
Tubal ligation– Women who have undergone the tying of their fallopian tubes may be at low risk of suffering from ovarian cancer.
Preventive surgery- Preventive surgery may include surgical removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes in individuals with an extremely high risk of developing it, for example, in women with known mutations in the BRCA genes to avoid developing ovarian cancer.
Conclusion
Ovarian cancer is a serious and complex disease that has affected thousands of women per year. Although this term describes “silent killer” due to its subtle symptoms, awareness can help with identifying the issue sooner and improve outcomes. Improvements in treatment options, ranging from surgical, and medical management consisting of chemotherapy and targeted therapy to more recent immunotherapy, promise better management and survival.
This research might be basic in the identification and treatment of ovarian cancer. On their part, women should keep informed, find out the ovarian cancer symptoms, and then discuss any beliefs with doctors. Ovarian cancer survival rate has to improve since early detection is possible. Hence, for every woman, awareness and proactive health care become all-important.
Disclaimer
In this article, information related to a particular topic has been collected from various sources and the internet, the purpose of which, is only to increase the knowledge of the readers and it does not confirm the existence of any disease, particular statement, explanation, appropriateness, congruity, and information or any kind of treatment. Health Alpha does not take any responsibility for any such information.
Views: 6