
The olive is a small fruit of the Olive tree, culturally and historically highly important for over a thousand years. Because of its multi-use purposes, nutritional value, and symbolic meaning, it grew to be one of the most cherished fruits among various cultures.
Table of Contents
Scientifically known as Olea europaea, it is one of the major strands in Mediterranean cuisine and culture, symbolizing peace, wisdom, and prosperity. It is in this light that this blog post takes a look at the olive from all its sides: cultivation, different olive oil production processes, and its culinary and health benefits.
A Brief History of the Olive
It is believed to be indigenous to a region in the Mediterranean Basin and was first cultivated more than 6,000 years ago. Archaeological evidence indicates that olives were first domesticated in a region that includes present-day Turkey, Syria, and Palestine.

To the ancients, especially the Greeks and the Romans, the olive tree was a highly regarded plant and was even considered a gift from the gods Athena and Zeus, respectively. The olive branch, with its sense of peace, famously came into Greek mythology when Athena bestowed an olive tree upon the city of Athens, thereby bringing prosperity to its inhabitants.
The olive and its oil have played a significant part in the history of many cultures. The Bible and Quran mention the olive tree, which evidences the significance it possesses in a religious framework. The tree thus finds application as a backbone of many economies, since olive oil was an extremely valuable commodity traded all over the world and a staple in ancient people’s diets.
The Olive Tree: Planting and Varieties

Olive tree – a very hardy plant indeed, olive trees thrive in warm temperate climates with well-drained soil. It is resistant to drought conditions; hence, the main characteristic that enables this evergreen to survive in the Mediterranean’s hot, dry summers.
Under good conditions, the olive tree may live for hundreds, and in some cases even thousands, of years. Many trees in the Mediterranean are estimated to be centuries old and, even today, remain in production.
There are hundreds of distinct olive varieties identified, which all offer quite varied flavors, sizes, and oil contents. Among the more famous olive varieties include:
Kalamata
Native to Greece, these are large purple olives renowned for their full-bodied, fruity flavor. Often used in salads, particularly Greek salad, and a table olive.
Manzanilla
This Spanish olive is somewhat smaller, with a nutty flavor. It is usually brined and sold as a green table olive, or it might be stuffed with pimentos.
Arbequina
A brown olive from Spain, the Arbequina olives are used primarily for olive oil production due to their high oil content and delicate flavor.
Mission
Originating in California, Mission olives serve both table olive and olive oil purposes. They are often cured with lye and possess a mild, slightly fruity flavor.
Olive Harvesting Procedure
The general period for olive harvest falls from late summer to early winter, depending on the variety and use. Table olives are picked when they reach complete size but before actual maturity occurs, at which time they are firm in texture and only slightly bitter. Olives used specifically for oil are usually picked at a fully ripe stage when they have a higher oil content and reflect a more complex flavor profile.
The fact is that olives are one of the more labor-intensive fruits to harvest, by either traditional hand-picking methods or by more modern ways using mechanical harvesters. Olives must be processed within a fairly short period from harvesting to avoid spoilage and ensure quality. In table olives, this entails curing, which removes bitterness inherent in the raw olive. There are several curing methods, including brining, dry curing with salt, or even lye curing.
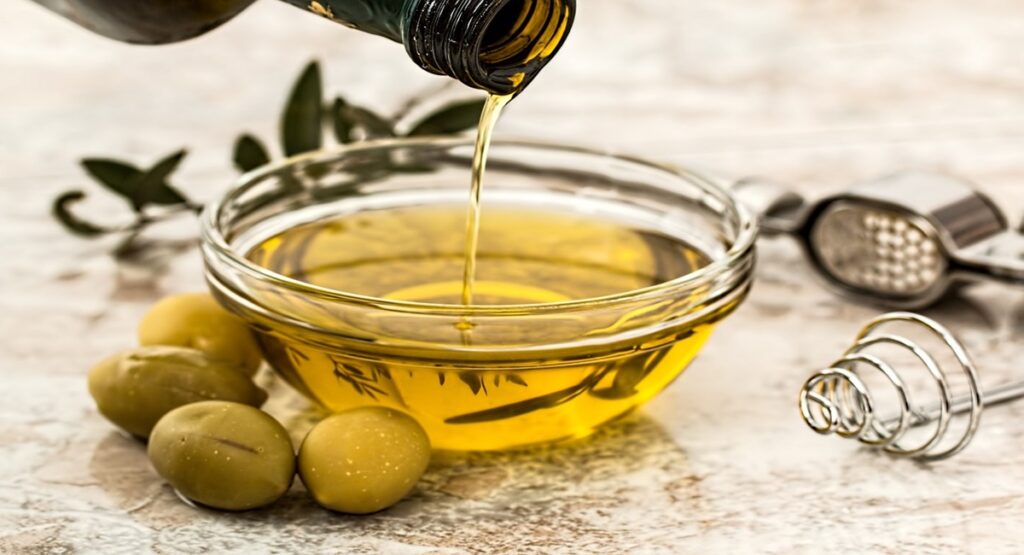
The Olive Oil-the Liquid Gold of the Mediterranean
Of all, one of the most valued products derived from olives is olive oil, also referred to as “liquid gold.” This is a major product in the Mediterranean diet, highly valued for its taste and as a source of many health benefits. The product was extracted by crushing olives into juice and then separating oil from water and solids.
Types of Olive Oil
1-Extra Virgin Olive Oil
This is the highest-grade olive oil, and it is produced solely using mechanical methods without heat or chemicals. EVOO has an incomparable taste due to a low acidity level (less than 0.8 percent), retaining most of the natural flavors and antioxidants found in olives.

2-Virgin Olive Oil
Similarly extracted through mechanical means, virgin olive oil resembles the EVOO variety but can contain as much as 2% acidity level and minor defects in sensory. Still, good quality, though less flavorful than extra virgin olive oil.
3-Refined Olive Oil
This is the oil obtained by the refinement process of virgin olive oil to take away impurities and defects. Though refined olive oil has a more neutral flavor and longer shelf life, this lacks those antioxidants and has a rich taste compared to virgin oils.
4-Pomace olive oil
This is the lowest-grade olive oil, produced from the pomace that remains after the initial extraction. It undergoes refinement and is often blended with a small amount of virgin olive oil to enhance flavor. Pomace oil has widespread use in industrially manufactured food and for frying.
Health Benefits of the Olive and Olive Oil
There are many health benefits associated with olive oil, and this fact has been studied and documented quite well. Large intakes of olive oil, being part of the Mediterranean diet, have thus been associated with a reduced risk of chronic diseases related to cardiovascular disease, stroke, and cancers of the breast, colon, prostate, and ovary.
1-Nutritional Benefits of Olives
Olives are rich in monounsaturated fats, primarily oleic acid, which has been proven to lower LDL cholesterol while raising HDL cholesterol. They also contain vitamin E, a very powerful antioxidant that is highly important to protect cells, among other essential nutrients like iron, copper, and calcium.
2-Cardiovascular health
High proportions of monounsaturated fat, combined with other antioxidants such as polyphenols in olive oil, serve to reduce inflammation, improve blood pressure, and generally keep the heart in good condition. Indeed, many studies identify habitual consumption of olive oil with reduced risks of cardiovascular diseases.
3-Anti-Inflammatory Properties
The polyphenols in olive oil show a very strong anti-inflammatory action, similar to that produced by ibuprofen. Thus, olive oil is indicated as a better option for patients suffering from chronic disorders of inflammation, such as arthritis.
4-Antioxidant Powerhouse
“Olive oil is a real antioxidant powerhouse”; it consists of antioxidants that neutralize oxidative stress and protect cells from any damage. This antioxidant is responsible for anti-aging properties, making the skin healthy and resulting in a reduced risk of chronic diseases.
5-Cognitive Health
That may hold some proof as far as mental health as far as olive oil consumption protecting against the development of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease. The antioxidants in olive oil can help prevent the oxidative damage that causes cognitive loss.
Culinary Uses of the Olive and Olive Oil
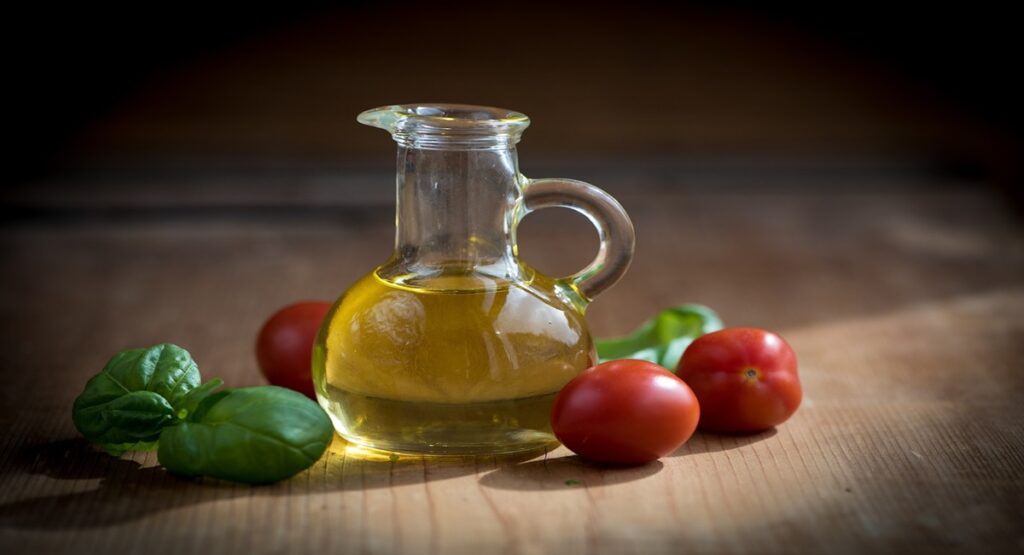

Olives and their oil are at the very core of Mediterranean cuisine. Both add depth and flavor to everything from simple snacks comprised of olives and olive oil to salads, tapenades, stews, and pasta dishes. Olives marry well with cheese, nuts, and wine, thus appearing on many appetizer plates.
Olive oil is a versatile cooking oil that works great for everything from drizzling over salads and roasting vegetables to sautéing and even baking. Rich in fruitier flavor notes, it adds depth to dishes and gives simplicity a touch of finesse. In this respect, extra virgin olive oil often finds itself at the end of dishes as a finishing oil, drizzled over right before serving to give its unique flavor.
Conclusion
The olive is considered the symbol of peace, wisdom, and prosperity, not to mention a lot of health benefits in this delicacy. From the millennial trees that survive time, to the golden olive oil that adorns our tables, it continues to be an integral part of diet and culture. This is eaten as a plain snack, part of a more involved dish, and even yields a healthy oil; it is a timeless, cherished fruit that seems to enrich our lives while connecting us with the rich heritage of the Mediterranean.
In adopting the olive and applying its oil in our daily existence, we are continuing a tradition that has nourished and sustained mankind for several millennia. The olive tree and its precious fruit remind us of our common past and the inseparable link between nature, culture, and health.
Disclaimer
In this article, information related to a particular topic has been collected from various sources, the purpose of which is only to increase the knowledge of the readers and it does not confirm the existence of any disease and its treatment. Health Alpha does not take any responsibility for any such information.
Views: 12











Pingback: Bottle Gourd Juice-12 boons.Bland flavor?Go and try it today