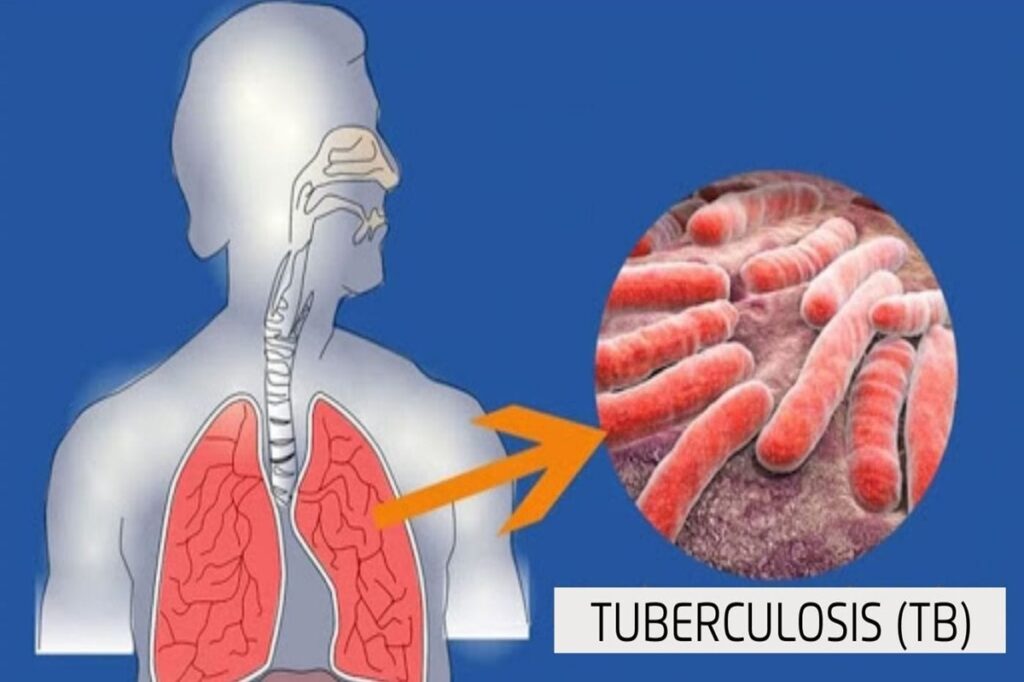
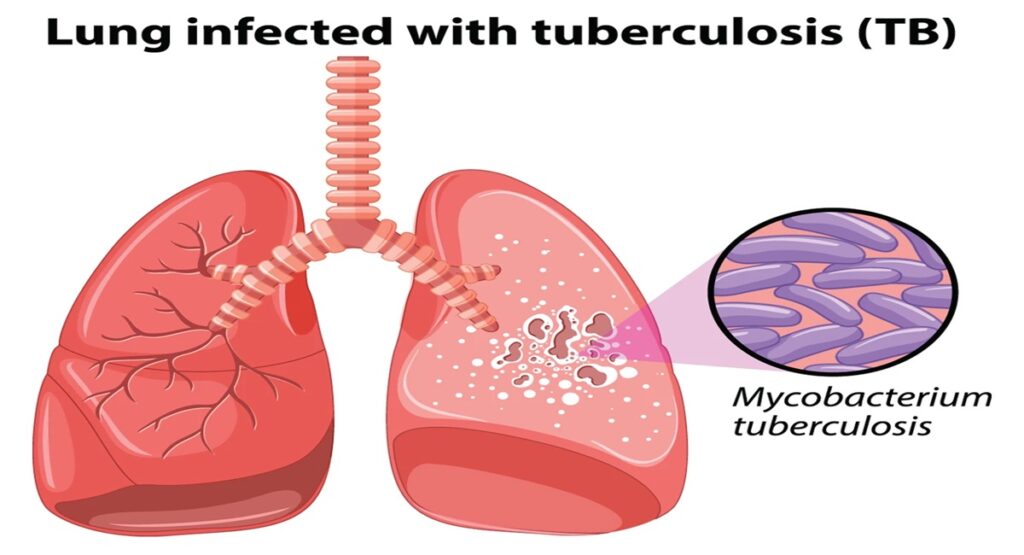
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Usually, this bacteria affects the lungs, but TB bacteria can affect any part of the body such as the kidneys, spine, and brain. Not every person who has the TB bacteria gets sick.
Table of Contents
If a person has been infected with tuberculosis and does not receive proper treatment, TB disease can prove fatal for that person. Knowing about the symptoms and treatment of TB will help you a lot. In this article, we discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment of TB in detail.
What is Tuberculosis (TB)?
TB is called Tuberculosis in the English language. TB is an infectious disease, which spreads from one person to another through breathing. Many symptoms arise due to this disease, which you are going to know through this blog. As we have told you earlier this disease is spread by a bacteria called Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. The main reason behind the spread of TB is air. TB can spread from one infected person to another through cough, sneeze, or saliva.
The main function of this bacteria is to damage our lungs. This disease affects those parts of our body where the amount of blood and oxygen is high. This is why most cases of TB are lung infections. TB in the lungs is also called pulmonary TB.
Types of Tuberculosis (TB)
Many types of TB diseases trouble a person like –
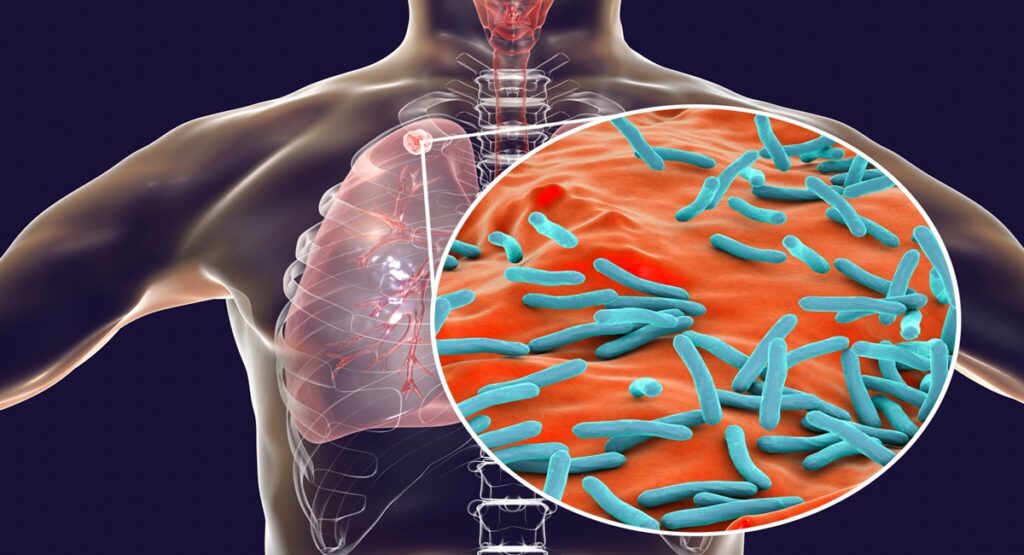
Latent TB
In this type of TB, the bacteria remain in the body in inactive form, because the strong immunity of the body does not allow it to become active. In this condition no symptoms of TB are visible. But in the future, it may become active, which can cause a lot of problems.
Active TB
In this type of TB, bacteria are produced inside the body and all the disease symptoms are seen in it. This is an infectious type of disease.
Pulmonary TB
This type of TB can be considered as the initial (primary) form of this disease, which directly affects the lungs, causing prolonged cough.
Extra Pulmonary TB
In this type of TB, the disease spreads from the lungs to other parts as well. Along with the lungs, this problem can also spread to the bones, kidneys, and lymph nodes.
Symptoms of Tuberculosis
The location of the TB bacteria’s growth within the body determines the symptoms of tuberculosis. Though most of the disease’s symptoms are distinct from one another, there are rare instances where bone TB differs from throat TB. The lungs are where TB germs typically thrive (pulmonary TB). The following symptoms may occur in the case of TB –
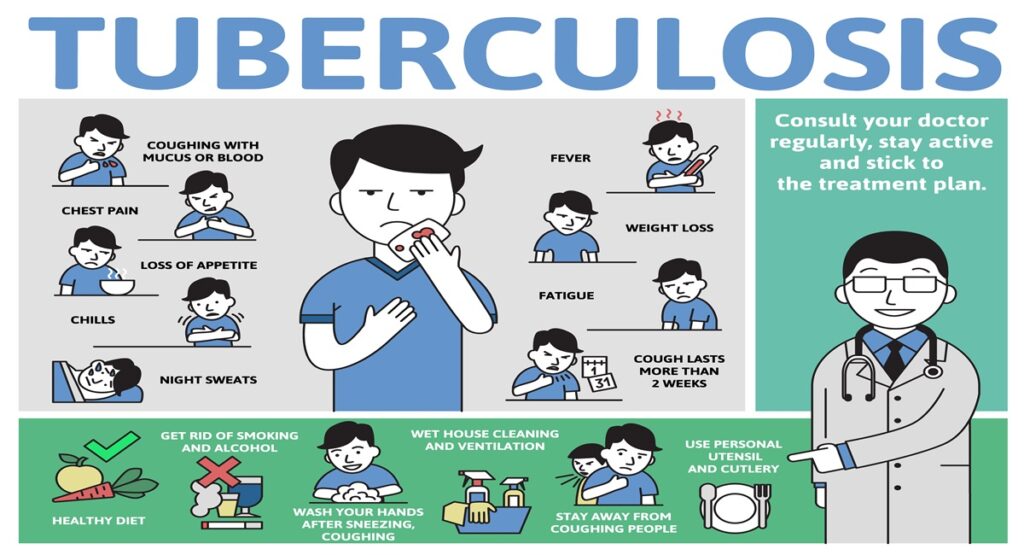
1- Cough problem that persists for 3 weeks or more.
2- Chest pain.
3- Bleeding in phlegm.
4- Weakness or fatigue.
5- Weight loss
6- Loss of appetite
7- Feeling cold
8- Fever
9- Night sweats
Many people misunderstand that the symptoms of TB in women are different from the symptoms of TB in men. But it is nothing like that. If you are facing any of the symptoms mentioned above, we would advise you to immediately seek medical help and defeat a serious problem like TB.
Why does TB occur?
TB is caused by bacteria, which spread through the air like the cold or flu. You get TB only when you come in contact with people who have the disease. If you are hanging out with someone who has TB and he sneezes without covering his mouth and a few drops of that sneeze land on you, then you can also suffer from that disease.
Treatment of Tuberculosis
Treatment of TB disease depends on the type of TB. If you have latent TB, your doctor may give you some medicine to kill the bacteria, so the infection does not become active. You may receive isoniazid, rifapentine, or rifampin salt medications alone or in combination. These types of medicines have a course, completion of which is extremely mandatory. If you notice any symptoms of active TB, immediately contact your pulmonology doctor and seek treatment.
Apart from this, the doctor may also suggest a combination of some medicines. Doctors usually use a combination of drugs called ethambutol, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and rifampin. The course of this medicine lasts for 6 to 12 months. Whereas in the case of pulmonary and extrapulmonary TB, the course of medicine becomes a little longer.
If you have any kind of infection or are on any kind of medication, then definitely inform the pulmonology doctor about it. Along with this, do not stop the course of medicines completely. If you skip the medications, the bacteria will become active again and the condition will become even worse.
TB prevention measures
Along with the treatment of TB, prevention is also equally important. The following measures can be taken to help prevent the spread of TB –
(a)-If you have latent TB, take all your medicines on time so that it does not become active and infectious and you get better quickly.
(b)-Regarding active TB, the patient himself should avoid coming in contact with other people. Cover your mouth when you laugh, sneeze, or cough. Even if you meet someone, be sure to wear a surgical mask.
(c)- If you’re traveling to a place where TB is common, try to avoid crowded areas.
(d)- Take special care of your diet like – promoting the consumption of khichdi, milk, cheese, fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and green tea.
(e)- In the case of TB, the most important thing is to listen to the doctor and complete your treatment course.
FAQ
1- Is a permanent cure for Tuberculosis (TB) possible?
With treatment, TB can be cured almost permanently. Usually, a course of antibiotics lasts for 6 months. Many different antibiotics are used, as different types of TB are resistant to some antibiotics.
2- How many days does TB treatment last?
Most people with TB disease take at least 6 months to recover. But even during this period, it is not advisable to stop taking the medicine.
3-How many days does the treatment of pulmonary TB last?
Regular treatment for 6 months is necessary. In complicated cases, pulmonary TB may take up to 9 months to be cured. Pulmonary TB is almost always curable by taking medicines regularly.
4- How to identify a TB patient?
Cough for more than 3 weeks, fever, night sweats, weight loss – these are the symptoms that can identify a TB patient. Skin or blood tests can confirm the condition.
5- In how many days does TB medicine take effect?
Therefore, you will have to take TB drugs for at least 2 to 3 weeks before you become unable to transmit TB germs to others. Even if you start feeling better, you will need to stay on the medicine to recover. You will have to take several types of pills for at least 6 months.
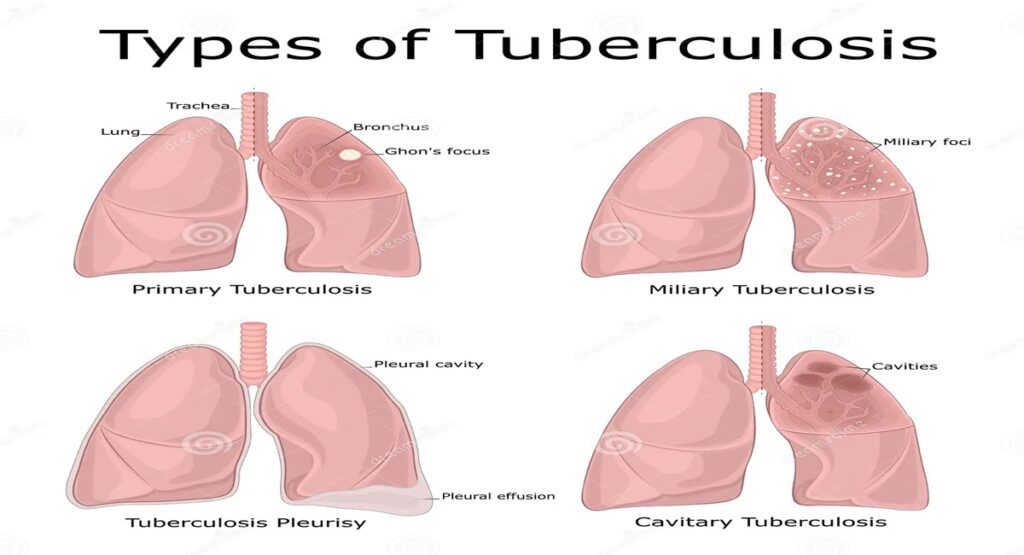
6- How many types of TB are there?
There are mainly four types of TB such as –
Latent TB
Active TB
Pulmonary TB
Extra Pulmonary TB
7- How is TB spread?
TB is an infectious disease, which spreads through contact with an infected person. If you come in contact with someone who has TB, there is a high possibility that you too may suffer from this disease.
8- Tuberculosis is spread by which bacteria?
The reason behind the occurrence of tuberculosis is a bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It is an infectious bacteria that affects a person through exposure to infected air.
9- Is TB a fatal disease?
Yes, TB is a fatal disease. In this disease, bacteria can affect the lungs, brain, bones, and other organs of the body. But a timely cure can save a life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, tuberculosis is one of the paramount health-related issues in the world that demands a lot of awareness and proactive measures to ensure good management. It entails awareness of tuberculosis symptoms to ensure early detection and treatment. Some common signs include a persistent cough for more than three weeks, chest pains, coughing up blood, loss of weight without apparent reason, fever, and night sweats, which may remind one of the symptoms to seek medical attention in time before the disease spreads.
This requires a need to understand how is tuberculosis spread. The process through which the TB bacteria are transmitted is when an infected person coughs or sneezes and others inhale the bacteria from the droplets that were emitted. This mainly explains why public health measures need to be implemented together with education in terms of stopping outbreaks and conserving at-risk populations.
There are several alternatives for the treatment of TB: there are several tuberculosis treatment options. One of the most frequent treatments is a long-term regime of antibiotics, which will kill all bacteria in the body. Finishing the prescribed course of treatment is of the utmost necessity so that drug-resistant forms of TB cannot be created.
Finally, preventing tuberculosis is a major public health strategy. It carries with it some degree of protection against serious and deadly tuberculosis in children. Improvements in living conditions, ventilated crowded places, and making people aware of tuberculosis can also help to reduce its circulation to a great extent.
This would enable patients and communities to collaborate and combat this disease effectively. With the knowledge of the symptoms, modes of transmission, treatment options, and prevention strategies of tuberculosis, the life and community can be changed toward becoming healthier.
Disclaimer
In this article, information related to a particular topic has been collected from various sources, the purpose of which, is only to increase the knowledge of the readers and it does not confirm the existence of any disease, particular statement, explanation, appropriateness, congruity, and information or any kind of treatment. Health Alpha does not take any responsibility for any such information.
Views: 1